DBMS Introduction
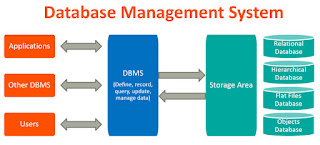
A database management system (DBMS) refers to the technology for creating and managing databases. DBMS is a software tool to organize (create, retrieve, update and manage) data in a database.
DBMS AIM :
The main aim of a DBMS is to supply a way to store up and retrieve database information that is both convenient and efficient. By data, we mean known facts that can be recorded and that have embedded meaning. Normally people use software such as DBASE IV or V, Microsoft ACCESS, or EXCEL to store data in the form of database. A datum is a unit of data. Meaningful data combined to form information. Hence, information is interpreted data - data provided with semantics. MS. ACCESS is one of the most common examples of database management software.
DBMS KNOWLEDGE
Database systems are meant to handle a large collection of information. Management of data involves both defining structures for storage of information and providing mechanisms that can do the manipulation of those stored information. Moreover, the database system must ensure the safety of the information stored, despite system crashes or attempts at unauthorized access.
why use DBMS?
- To develop software applications In less time.
- Data independence and efficient use of data.
- For uniform data administration.
- For data integrity and security.
- For concurrent access to data, and data recovery from crashes.
- To use user-friendly declarative query language.
ADVANTAGES OF DBMS
A DBMS manage data and has many advantages. These are:
- Data independence: Application programs should be as free or independent as possible from details of data representation and storage. DBMS can supply an abstract view of the data for insulating application code from such facts.
- Efficient data access: DBMS utilizes a mixture of sophisticated concepts and techniques for storing and retrieving data competently, and this feature becomes important in cases where the data is stored on external storage devices.
- Data integrity and security: If data is accessed through the DBMS, the DBMS can enforce integrity constraints on the data.
- Data administration: When several users share the data, integrating the administration of data can offer major improvements. Experienced professionals understand the nature of the data being managed and can be responsible for organizing the data representation to reduce redundancy and make the data to retrieve efficiently.





0 Comments